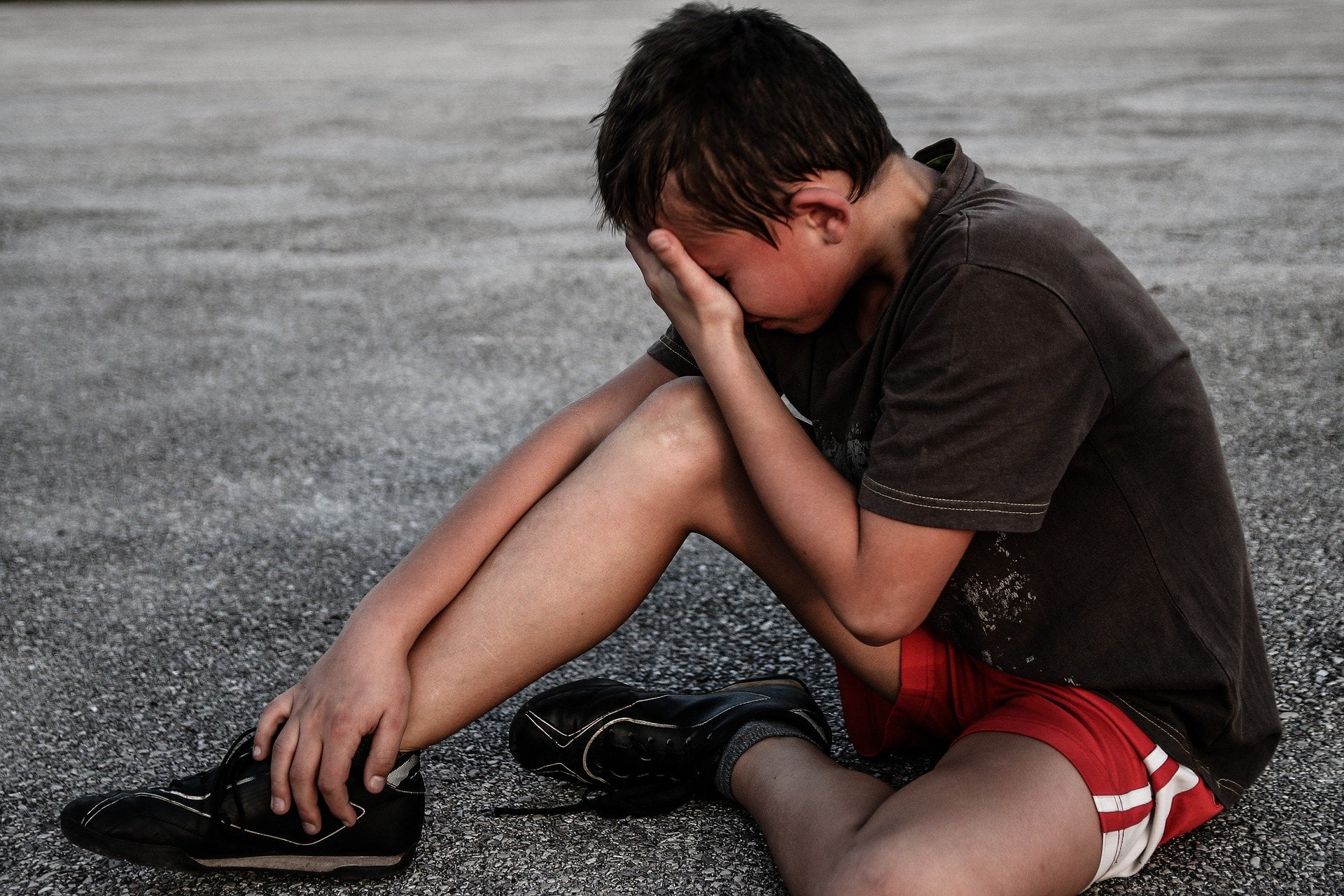
If you are a parent, you want to do everything within your power to ensure that your child is pain-free. But first, you need to know how if your child is in pain. We will explain how chronic child pain can be detected and what causes it.
Chronic pain in children is common and can be managed effectively. Pain can occur after a specific event such as injury, viral infection, or may not have an apparent cause.
Recovery can take time and require significant medical interventions and family support, and sometimes there are no quick solutions to eliminate the pain. Proper pain management is required for children.
It is estimated that 20% to 35% of children and adolescents are affected by chronic pain. It consists of a variety of pain syndromes.
Recurrent abdominal pain is defined as pain severe enough to interfere with activity. It is very common, affecting around 10% of school-aged children.
Recurrent headaches are also common, affecting as many as 10% of school-aged children.
Migraine and tension headaches are the most common types.
How can you detect pain in children?
The initial evaluation should involve taking a complete medical and pain history including onset, intensity, frequency, duration, variability, aggravating, and alleviating factors.
A psychosocial assessment can be done. It focuses on the child’s emotional functioning skills, the impact of pain on daily life (including sleep patterns, eating, school, social and physical activities), and family and peer group interactions.
This is also known as Psychometrics. What is psychometrics? Click here to know more!
There is a range of behavioral distress scales available for infants based on facial expression, crying, and body activity. The facial expression appears to be the most useful indicator to assess pain severity.
From the age of three and upwards, children become increasingly capable of describing the intensity, location, and quality of pain. Drawing, pictures of faces, or graded color intensity can be used. A numeric rating scale can also be used for severity.